

Next: Result
Up: Materials and Methods
Previous: Gel shift assay
To express the His-tagged
PF1684 protein, we subcloned the PF1684 gene into the pET-23b expression vector
by PCR using region-specific oligonucleotides as primers. These oligonucleotides
were designed to provide PCR products with NdeI and XhoI sites at the
5'- and 3'- termini respectively. The resulting construct (termed pET-PF1684) contained
the sequence coding for the PF1684 protein and six consecutive histidine
residues (His-tag) at the C-terminus to be used as an affinity tag for
purification. The nucleotide sequence of the insert was confirmed to be the
original sequence. Recombinant PF1684 protein was overexpressed in E. coli
strain BL21 (DE3) under the control of the phage T7 promoter. Protein was then
extracted by sonication (30 s) in a buffer containing 20 mM Tris/HCl (pH 8.0),
500 mM NaCl, 5 mM imidazole and 0.1% Triton X-100. The extract was heat-treated
at 80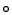 C for 15 min to denature endogenous E. coli proteins and then centrifuged
at 12000 g for 10 min at 4
C for 15 min to denature endogenous E. coli proteins and then centrifuged
at 12000 g for 10 min at 4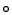 C to separate the cell debris from the extract. The
PF1684 protein was purified using a 5 ml Ni2+-Sepharose column according to the
manufacturer's instructions (Novagen). The protein with peak RNA-binding
activity was purified further by dialysis. SDS/PAGE showed that the purity of
the PF1684 protein in the final preparation approached near homogeneity. 2.5
Determination of protein concentration Bio-RadŐs protein assay system was used
to check the protein concentration based on the color change of Coomassie
Brilliant Blue G-250 dye in response to various concentrations of protein. 2.6
DNA Sequencing The sequencing reaction was performed by PCR. The PCR product was
then purified by chromatography (Centri-Sep) then sequenced by the sequencer
(ABI 3100 Genetic Analyzer).
C to separate the cell debris from the extract. The
PF1684 protein was purified using a 5 ml Ni2+-Sepharose column according to the
manufacturer's instructions (Novagen). The protein with peak RNA-binding
activity was purified further by dialysis. SDS/PAGE showed that the purity of
the PF1684 protein in the final preparation approached near homogeneity. 2.5
Determination of protein concentration Bio-RadŐs protein assay system was used
to check the protein concentration based on the color change of Coomassie
Brilliant Blue G-250 dye in response to various concentrations of protein. 2.6
DNA Sequencing The sequencing reaction was performed by PCR. The PCR product was
then purified by chromatography (Centri-Sep) then sequenced by the sequencer
(ABI 3100 Genetic Analyzer).


Next: Result
Up: Materials and Methods
Previous: Gel shift assay
Xiaojing (Lucy)
2005-02-06