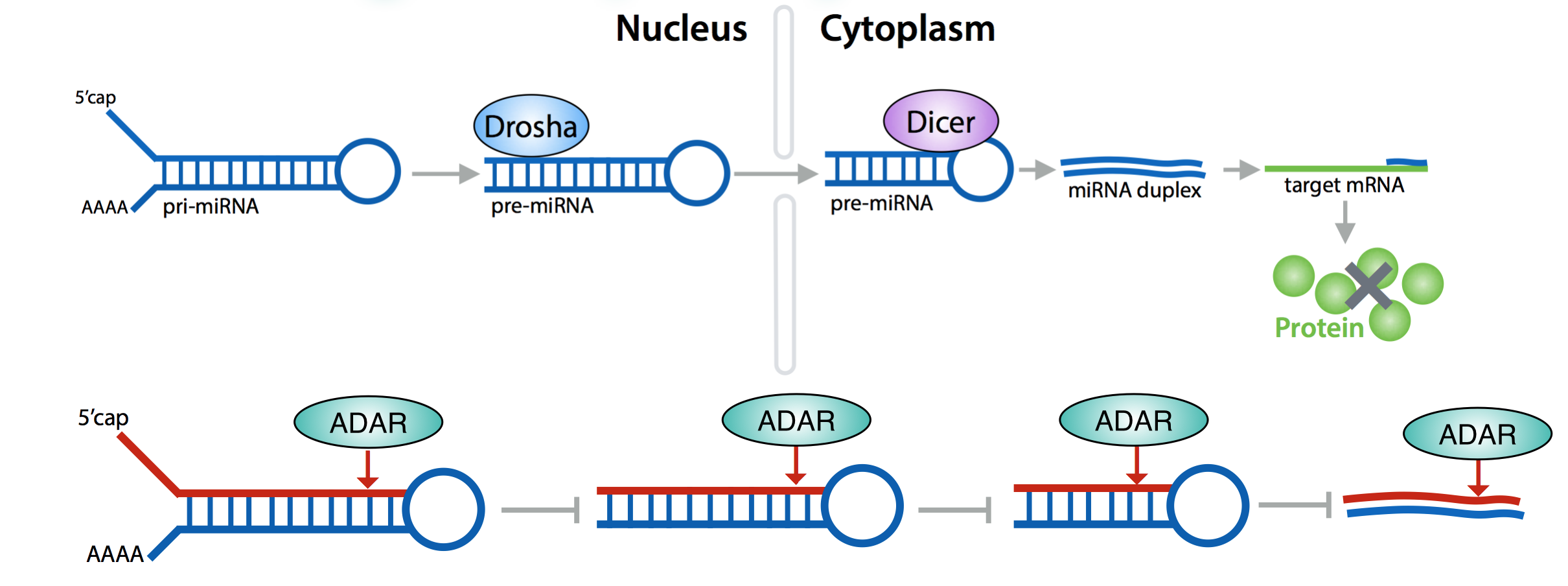

Adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editing is catalyzed by a family of adenosine deaminases acting on RNAs (ADARs) which comprises three active isoforms in human. A-to-I editing within a coding region is known to change the amino-acid sequence in the protein product, which is essential for the proper activity of certain neurotransmitter receptors. However, most A-to-I editing events occur within non-coding transcripts, and contributes to post-transcriptional gene regulation such as splicing, translation, miRNA processing. For ADAR isoform-specific genome-wide identification of A-to-I editing sites on pre- and mature miRNAs, we conducted an RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (RIP-seq) approach using GFP-tagged ADAR expression constructs in HeLa cells. After stringent and careful read mapping and filtering steps, we identified many novel A-to-I editing candidate sites on mature and pre-miRNAs, and revealed that the majority of editing sites concentrated in the miRNA seed region, which is responsible for target recognition by sequence complementarity. Furthermore, our data also suggest a difference in the editing site motif preferences by each ADAR isoform. To confirm the candidate sites experimentally, we performed adaptor-ligated RT-PCR procedure (Kawahara et al. 2012). We shall present the results of this investigation, and discuss the implications of these findings on the regulation of miRNA activity.
※ なお、本研究は、東京大学理学系研究科 程研究室との共同研究かつ執筆論文が未発表のため、図表および詳細に関する報告を控えさせて頂きます。